Before 2000, Japan occupied a leading position in the global battery market. However, in the 21st century, Chinese and Korean battery enterprises rose rapidly with low cost advantages, forming a strong impact on Japan, and the global market share of Japanese battery industry began to decline. Facing the fact that the competitiveness of Japanese battery industry was gradually weakening, the Japanese government issued relevant strategies for many times to promote the development of battery industry.
- In 2012, Japan issued Battery Strategy, setting the strategic goal of Japan’s global market share reaching 50% by 2020.
- In 2014, Auto Industry Strategy 2014 was announced to clarify the important position of battery in the development of electrical vehicles.
- In 2018, the “Fifth Energy Basic Plan” was released, emphasizing the importance of batteries in the construction of “decarbonization” energy systems.
- In the new version of 2050 Carbon Neutralization Green Growth Strategy in 2021, the battery and automobile industry are listed as one of the 14 key development industries.
In August 2022, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) issued a new version of Battery Industry Strategy, which summarized the development experience and lessons of Japanese battery industry since the implementation of Battery Strategy in 2012, and planned detailed implementation rules and technical road map.
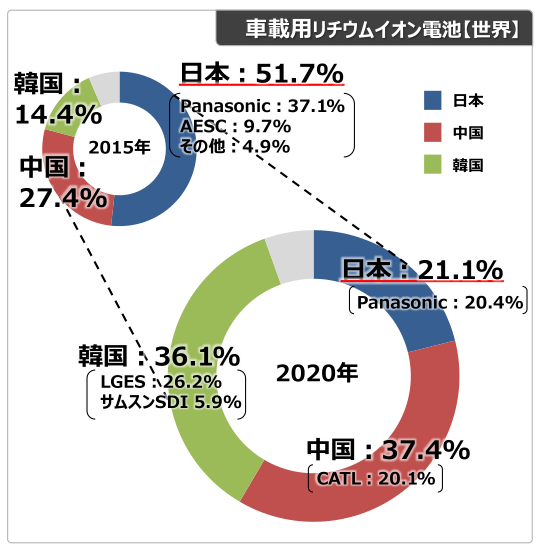
The market share of power batteries of Japanese enterprises has declined.
Financial support for batteries from various countries.
Governments of major countries have implemented large-scale policy support for batteries. In addition, Europe and the United States have promoted sustainable battery supply chains through restrictive and tax measures.
U.S.
- 100-day lithium battery supply chain review;
- ¡ US $2.8 billion in support of domestic battery manufacturing and mineral production;
- Products with a high proportion of battery materials and components purchased from North America or FTA contracting countries will be subject to preferential EV tax treatment, in light of the Inflation Reduction Act.
Europe
- The establishment of the European Battery Alliance (EBA) with participation of 500 companies;
- Battery, material factory financial support and technical development support;
- Carbon footprint limits, responsible mineral surveys, and restrictions on recycling materials under (EU)2023/1542.
South Korea
- ‘K Battery Development Strategy’: tax incentives, investment tax relief
China
- New energy vehicle incentive;
- Support for battery factories and reduced income tax rates (from 25 percent to 15 percent) for companies that meet certain standards
Reflection on past policies
- So far the battery policy and the primary strategy is to focus on investment in all solid battery technology development.
- In recent years, with the strong support of governments, Chinese and Korean enterprises have caught up with Japan in liquid lithium-ion battery (LiB) technology, especially in aspect of cost, which has surpassed Japan in international competitiveness. Capital and private investment competition in the world, including Europe and the United States, is becoming increasingly fierce. Although progress has been made in technology development of all-solid-state batteries, there are still problems to be solved in the future, and it is expected that the liquid LiB market will continue for some time.
- Japanese companies focus only on the domestic market, not fully consider the development of the global market. In this way, before all-solid-state batteries are put into practice, Japanese companies will be exhausted and may withdraw from the market.
Future promotion strategy
- Expand and refine domestic policy to establish Japan’s annual manufacturing capacity of 150GWh by 2030
- The Battery Industry Association (BAJ) will also launch a series of cooperation with organizations such as the Japan Electrical Industries Association (JEMA), aiming to reduce costs and increase product added value, and promoting battery system integration research.
- The Japan Battery Supply Chain Association (BASC) will track the latest progress of industry investment for member companies, in order to promote the government and private sector to jointly strengthen the investment in domestic battery and material manufacturing base.
- To create new advantages in cutting-edge battery manufacturing technology and advanced manufacturing processes by promoting digital transformation (DX) and green transformation (GX)
- Strategic formation of global alliances and global standards
- It will carry out active dialogue and cooperation with more countries (regions) in the global supply chain of batteries, research and development, information exchange, and the formulation of rules related to battery sustainability, and accelerate the establishment of global strategic alliances. In addition, BASC conducts dialogue and cooperation with relevant groups overseas from the perspective of supply chain cooperation and international institutional coordination. To ensure the supply and recycling of metal materials for batteries, the construction of battery digital solutions and other commercial infrastructure.
- To promote the establishment of international standards, such as carbon footprint calculation methods, due diligence, international discussions on sustainability. For the IEC 63369 meeting on the CFP carbon footprint calculation method for lithium batteries, BAJ will devote to develop standards that reflect Japan’s claims.
- After the proposed adoption of mandatory internal short circuit test and simulated combustion test (IEC 62619), BAJ will continue to lead the discussions on domestic and international standardization of battery safety, functionality, etc.
- BAJ will cooperate with NITE (Japan’s National Technical Infrastructure for Product Evaluation) to explore how to evaluate the safety and functionality of batteries. In addition, JEMA will also explore the international promotion of the solutions that utilize distributed power sources including Japanese-made batteries.
- Development of battery utilization for new purposes and related services. For example, the global market potential of electric ships, aircraft, agricultural machinery, etc. and explore the support for batteries to gain overseas markets and promote the entry of new businesses. In addition, the promotion of V2X led by V2H (Vehicle to Home) will also be discussed.
- Ensure upstream resources
- To secure the support on the resources for the companies (expansion of investment and other sub-policy, strengthening debt guarantee function (relaxing the completion guarantee conditions)). To strengthen cooperation between enterprises and battery user companies, manufacturers, government financial institutions, etc., and to explore plans to build a system to ensure rights and interests.
- In order to ensure rights and interests, the cooperation with relevant countries will be strengthened by holding investment seminars and private-public joint meetings with resource-owning countries (Australia, South America, Africa, etc.) to secure upstream rights and interests.
- To promote international coordination of minerals. Every year BASC will conduct questionnaire surveys with member companies as the target to follow up the latest investment status of the industry.
- Development of new generation technology
- To promote research and development through industry-academia-government collaboration. To Strengthen the support for the technology development of next-generation battery through the Green Innovation Fund, etc. To accelerate the development of next-generation batteries and materials centered on all-solid-state batteries (including the development of material evaluation basis), and recycling technology development. Around 2030, aim to realize the practical use of all-solid-state batteries, as well as the technical advantages in new battery technologies including innovative batteries (halide, zinc anode batteries, etc.)
- To improve performance testing and safety evaluation facilities for next-generation batteries, etc.
- To strengthen linkage between research and development sites and human resources development on batteries and next-generation batteries included.
- Create domestic market
- To promote the spread of electric vehicles. By 2035, 100% of new passenger car sales will be electric vehicles, and actively support the purchase and charging infrastructure construction of electric vehicles.
- To promote the popularization of batteries for energy storage, and try to continue to develop new
- uses for batteries, explore new application areas, promote comprehensively the diversification of demand markets, and fully stimulate the development potential of the battery industry
- Regarding the energy storage system connected to the power grid system, considering that it will form part of the electric power infrastructure in the future, BAJ will cooperate with relevant groups to ensure the safety of the storage system and the safety required as electric power infrastructure.
- Strengthen talent training
- To establish “Kansai Battery Talent Training Center” in the Kansai region where battery-related industries are concentrated, and to use the Kansai Development Center’s advanced analysis equipment and battery manufacturing equipment to conduct field teaching.
- Strengthen domestic battery manufacturing and usage environment
- To set up the goal of a domestic recycling system before 2030, further understand the circulation of dismantled batteries, strengthen the recycling capacity of used batteries, Study and take measures to activate the reused battery market, and build a recycling foundation. BASC will promote recycling standardization and discussions on easy-to-recycle battery standards, etc. JEMA will jointly build recycling solutions for residential lithium-ion storage systems.
- To promote discussions on renewable energy supply and deployment methods that will help improve industrial competitiveness. It is also important to provide a good production environment for battery manufacturing (cheap land and electricity). In addition, discussions on plans to reduce Japan’s electricity bills will be promoted by controlling energy costs, etc.
- Revision of relevant regulations (Fire Protection Act). BAJ is also involved in plans of re-discuss the relevant provisions of the fire protection law, including: ① regarding the diversification and large-capacity of battery types (capacity 4800Ah, revising unit regulations); ②About re-evaluation based on battery equipment characteristics. (Because there are safety hazards such as fire for batteries, Japan’s Fire Protection Law considers them dangerous goods and strictly regulates the storage and installation of batteries. The applicable batteries regulated by the “Fire Protection Law” are industrial batteries with a capacity of 4800Ah (equivalent to 17.76kWh) or above.
- Unification of hardware and software interfaces related to manufacturing equipment
IN SUMMARIZE
Analysis from Japan’s new version of “Battery Industry Strategy”
1) Japan will re-emphasize the liquid lithium-ion battery market and strengthen the international competitiveness of batteries in the following three areas: sustainability (Carbon footprint, recycling, battery safety); Digital transformation (intelligent manufacturing and development, IoT integration, battery-related services, artificial intelligence) and green transformation (solid-state battery development, reducing energy consumption).
2) Japan will continue to develop its efforts in the field of solid-state batteries and plans for mass-production and putting into use of solid-state batteries in 2030.
3) To promote the popularization of electric vehicles in the domestic market and realize the electrification of all vehicles
4) To pay attention to battery recycling, formulate recycling standards, develop recycling methods, improve battery recyclability, etc.
From this battery industry policy, it can be seen that Japan has begun to realize the mistakes of their energy policy in the past. Meanwhile, the newly formulated policies are more in line with industry development trends, especially the recycling policies of all-solid-state batteries and battery.
Post time: Feb-02-2024